Abstract
Purpose
This study aimed to assess alterations in retinal vascular density in cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy (CADASIL) patients using optical coherence tomography angiography (OCTA) and investigate their association with MRI and cognitive features.
Methods
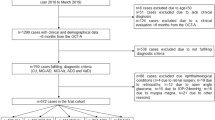
Twenty-five patients with CADASIL and forty healthy controls were evaluated by Cirrus HD-OCT 5000 with AngioPlex OCTA to determine changes in macular retinal vasculature. Retinal vasculature parameters between two groups were compared. The MRI lesion burden and neuropsychological scales were also examined in patients. The association between OCTA parameters and MRI/cognitive features was evaluated using partial Spearman rank correlation.
Results
The vessel density and perfusion density of whole image in macular region (vessel density: t = − 2.834, p = 0.005; perfusion density: t = − 2.691, p = 0.007) were significantly decreased in patients with CADASIL. Moreover, vessel density of whole image in macular region was negatively associated with Fazekas scores (ρ = − 0.457; p = 0.025) and the number of lacunar infractions (ρ = − 0.425, p = 0.038) after adjustment for age. Decreased macular vessel density and perfusion density of whole image were also associated with MoCA scores (vessel density: ρ = 0.542, p = 0.006; perfusion density: ρ = 0.478, p = 0.018) and other domain-specific neuropsychological tests (p < 0.05) after adjustment for age.
Conclusion
Decreased retinal vascular density was associated with increased MRI lesion burden and cognitive impairment in patients with CADASIL. Our findings suggest that the degree of retinal vascular involvement, as demonstrated by OCTA, may be consistent with the severity of MRI lesions and the degree of cognitive impairment in patients.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this manuscript will be made available by the corresponding authors, without undue reservation, to any qualified researcher.
References
Joutel A, Corpechot C, Ducros A, Vahedi K, Chabriat H, Mouton P, Alamowitch S, Domenga V, Cécillion M, Marechal E, Maciazek J, Vayssiere C, Cruaud C, Cabanis EA, Ruchoux MM, Weissenbach J, Bach JF, Bousser MG, Tournier-Lasserve E (1996) Notch3 mutations in CADASIL, a hereditary adult-onset condition causing stroke and dementia. Nature 383:707–710. https://doi.org/10.1038/383707a0
Yamamoto Y, Craggs LJ, Watanabe A, Booth T, Attems J, Low RW, Oakley AE, Kalaria RN (2013) Brain microvascular accumulation and distribution of the NOTCH3 ectodomain and granular osmiophilic material in CADASIL. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 72:416–431. https://doi.org/10.1097/NEN.0b013e31829020b5
Brice S, Jabouley A, Reyes S, Machado C, Rogan C, Dias-Gastellier N, Chabriat H, du Montcel ST (2020) Modeling the cognitive trajectory in CADASIL. J Alzheimer’s Dis : JAD 77:291–300. https://doi.org/10.3233/jad-200310
Roine S, Harju M, Kivelä TT, Pöyhönen M, Nikoskelainen E, Tuisku S, Kalimo H, Viitanen M, Summanen PA (2006) Ophthalmologic findings in cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy: a cross-sectional study. Ophthalmology 113:1411–1417. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ophtha.2006.03.030
Patton N, Aslam T, Macgillivray T, Pattie A, Deary IJ, Dhillon B (2005) Retinal vascular image analysis as a potential screening tool for cerebrovascular disease: a rationale based on homology between cerebral and retinal microvasculatures. J Anat 206:319–348. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-7580.2005.00395.x
Parisi V, Pierelli F, Malandrini A, Carrera P, Olzi D, Gregori D, Restuccia R, Parisi L, Fattapposta F (2000) Visual electrophysiological responses in subjects with cerebral autosomal arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy (CADASIL). Clin Neurophysiol 111:1582–1588
Parisi V, Pierelli F, Fattapposta F, Bianco F, Parisi L, Restuccia R, Malandrini A, Ferrari M, Carrera P (2003) Early visual function impairment in CADASIL. Neurology 60:2008–2010
Parisi V, Pierelli F, Coppola G, Restuccia R, Ferrazzoli D, Scassa C, Bianco F, Parisi L, Fattapposta F (2007) Reduction of optic nerve fiber layer thickness in CADASIL. Eur J Neurol 14:627–631
Haritoglou C, Rudolph G, Hoops JP, Opherk C, Kampik A, Dichgans M (2004) Retinal vascular abnormalities in CADASIL. Neurology 62:1202–1205. https://doi.org/10.1212/01.wnl.0000118296.16326.e1
Fang X-J, Yu M, Wu Y, Zhang Z-H, Wang W-W, Wang Z-X, Yuan Y (2017) Study of enhanced depth imaging optical coherence tomography in cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy. Chin Med J 130:1042–1048. https://doi.org/10.4103/0366-6999.204935
Liu Y, Wu Y, Xie S, Luan X-h, Yuan Y (2008) Retinal arterial abnormalities correlate with brain white matter lesions in cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leucoencephalopathy. Clin Experiment Ophthalmol 36:532–536. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1442-9071.2008.01825.x
de Carlo TE, Romano A, Waheed NK, Duker JS (2015) A review of optical coherence tomography angiography (OCTA). Int J Retina Vitreous 1:5. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40942-015-0005-8
Roberta F, Arturo C, Maurizio F (2022) Optical coherence tomography angiography of central serous chorioretinopathy: quantitative evaluation of the vascular pattern and capillary flow density. Graefe’s Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol = Albrecht Von Graefes Archiv Fur Klinische Und Experimentelle Ophthalmologie 260:1015–1024. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-021-05306-w
Carta A, Farci R, Galantuomo MS, Fossarello M (2022) X-linked retinoschisis: OCT-angiography in two brothers from a four-generation family with a p.Arg197Cys pathogenic variant in the gene. Eur J Ophthalmol 33:NP109-NP114. https://doi.org/10.1177/11206721221136315
Farci R, Carta A, Cocco E, Frau J, Fossarello M, Diaz G (2020) Optical coherence tomography angiography in multiple sclerosis: a cross-sectional study. PLoS One 15:e0236090. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0236090
Wang X, Wei Q, Wu X, Cao S, Chen C, Zhang J, Yan Y, Geng Z, Tian Y, Wang K (2021) The vessel density of the superficial retinal capillary plexus as a new biomarker in cerebral small vessel disease: an optical coherence tomography angiography study. Neurol Sci: Off J Italian Neurol Soc Italian Soc Clin Neurophysiol 42:3615–3624. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-021-05038-z
Fu W, Zhou X, Wang M, Li P, Hou J, Gao P, Wang J (2022) Fundus changes evaluated by OCTA in patients with cerebral small vessel disease and their correlations: a cross-sectional study. Front Neurol 13:843198. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2022.843198
Wu J, Zhang X, Azhati G, Li T, Xu G, Liu F (2020) Retinal microvascular attenuation in mental cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease by optical coherence tomography angiography. Acta Ophthalmol (Copenh) 98:e781–e787. https://doi.org/10.1111/aos.14381
Li Y, Wang X, Zhang Y, Zhang P, He C, Li R, Wang L, Zhang H, Zhang Y (2022) Retinal microvascular impairment in Parkinson’s disease with cognitive dysfunction. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 98:27–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2022.03.008
Fickweiler W, Wolfson EA, Paniagua SM, Yu MG, Adam A, Bahnam V, Sampani K, Wu IH, Musen G, Aiello LP, Shah H, Sun JK, King GL (2021) Association of cognitive function and retinal neural and vascular structure in type 1 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 106:1139–1149. https://doi.org/10.1210/clinem/dgaa921
Yang K, Cui L, Chen X, Yang C, Zheng J, Zhu X, Xiao Y, Su B, Li C, Shi K, Lu F, Qu J, Li M (2022) Decreased vessel density in retinal capillary plexus and thinner ganglion cell complex associated with cognitive impairment. Front Aging Neurosci 14:872466. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2022.872466
Yang K, Shen B, Li D-K, Wang Y, Zhao J, Zhao J, Yu W-B, Liu Z-Y, Tang Y-L, Liu F-T, Yu H, Wang J, Guo Q-H, Wu J-J (2018) Cognitive characteristics in Chinese non-demented PD patients based on gender difference. Transl Neurodegener 7:16. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40035-018-0120-1
Wardlaw JM, Smith EE, Biessels GJ, Cordonnier C, Fazekas F, Frayne R, Lindley RI, O’Brien JT, Barkhof F, Benavente OR, Black SE, Brayne C, Breteler M, Chabriat H, Decarli C, de Leeuw F-E, Doubal F, Duering M, Fox NC, Greenberg S, Hachinski V, Kilimann I, Mok V, Rv O, Pantoni L, Speck O, Stephan BCM, Teipel S, Viswanathan A, Werring D, Chen C, Smith C, van Buchem M, Norrving B, Gorelick PB, Dichgans M (2013) Neuroimaging standards for research into small vessel disease and its contribution to ageing and neurodegeneration. Lancet Neurol 12:822–838. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(13)70124-8
Fazekas F, Chawluk JB, Alavi A, Hurtig HI, Zimmerman RA (1987) MR signal abnormalities at 1.5 T in Alzheimer’s dementia and normal aging. AJR Am J Roentgenol 149:351–356. https://doi.org/10.2214/ajr.149.2.351
Ling C, Zhang Z, Wu Y, Fang X, Kong Q, Zhang W, Wang Z, Yang Q, Yuan Y (2019) Reduced venous oxygen saturation associates with increased dependence of patients with cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy: a 7.0-T magnetic resonance imaging study. Stroke 50:3128–3134. https://doi.org/10.1161/strokeaha.119.026376
Garcia-Medina JJ, Rubio-Velazquez E, Lopez-Bernal MD, Parraga-Muñoz D, Perez-Martinez A, Pinazo-Duran MD, Del-Rio-Vellosillo M (2020) Optical coherence tomography angiography of macula and optic nerve in autism spectrum disorder: a pilot study. J Clin Med 9:3123. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9103123
Nelis P, Kleffner I, Burg MC, Clemens CR, Alnawaiseh M, Motte J, Marziniak M, Eter N, Alten F (2018) OCT-angiography reveals reduced vessel density in the deep retinal plexus of CADASIL patients. Sci Rep 8:8148. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-26475-5
Tsokolas G, Tsaousis KT, Diakonis VF, Matsou A, Tyradellis S (2020) Optical coherence tomography angiography in neurodegenerative diseases: a review. Eye and brain 12:73–87. https://doi.org/10.2147/eb.S193026
Sun C, Wu Y, Ling C, Xie Z, Sun Y, Xie Z, Li Z, Fang X, Kong Q, An J, Wang B, Zhuo Y, Zhang W, Wang Z, Yuan Y, Zhang Z (2022) Reduced blood flow velocity in lenticulostriate arteries of patients with CADASIL assessed by PC-MRA at 7T. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 93:451–452. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp-2021-326258
Yu D-Y, Cringle SJ, Yu PK, Balaratnasingam C, Mehnert A, Sarunic MV, An D, Su E-N (2019) Retinal capillary perfusion: spatial and temporal heterogeneity. Prog Retin Eye Res 70:23–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.preteyeres.2019.01.001
Wei W, Li Y, Xie Z, Deegan AJ, Wang RK (2019) Spatial and temporal heterogeneities of capillary hemodynamics and its functional coupling during neural activation. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 38:1295–1303. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2018.2883244
Chan G, Balaratnasingam C, Yu PK, Morgan WH, McAllister IL, Cringle SJ, Yu D-Y (2013) Quantitative changes in perifoveal capillary networks in patients with vascular comorbidities. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 54:5175–5185. https://doi.org/10.1167/iovs.13-11945
Lin C-W, Yang Z-W, Chen C-H, Cheng Y-W, Tang S-C, Jeng J-S (2022) Reduced macular vessel density and inner retinal thickness correlate with the severity of cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy (CADASIL). PLoS One 17:e0268572. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0268572
Yoon SP, Grewal DS, Thompson AC, Polascik BW, Dunn C, Burke JR, Fekrat S (2019) Retinal microvascular and neurodegenerative changes in Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment compared with control participants. Ophthalmol Retina 3:489–499. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oret.2019.02.002
Li Z-B, Lin Z-J, Li N, Yu H, Wu Y-L, Shen X (2021) Evaluation of retinal and choroidal changes in patients with Alzheimer’s type dementia using optical coherence tomography angiography. Int J Ophthalmol 14:860–868. https://doi.org/10.18240/ijo.2021.06.11
Bulut M, Kurtuluş F, Gözkaya O, Erol MK, Cengiz A, Akıdan M, Yaman A (2018) Evaluation of optical coherence tomography angiographic findings in Alzheimer’s type dementia. Br J Ophthalmol 102:233–237. https://doi.org/10.1136/bjophthalmol-2017-310476
Ban S, Wang H, Wang M, Xu S, Qin Z, Su J, Du X, Liu J-R (2019) Diffuse tract damage in CADASIL is correlated with global cognitive impairment. Eur Neurol 81:294–301. https://doi.org/10.1159/000501612
Taniguchi A, Shindo A, Tabei KI, Onodera O, Ando Y, Urabe T, Kimura K, Kitagawa K, Miyamoto Y, Takegami M, Ihara M, Mizuta I, Mizuno T, Tomimoto H (2022) Imaging characteristics for predicting cognitive impairment in patients with cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy. Front Aging Neurosci 14:876437. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2022.876437
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge Yue Wu and Zhixin Li (Institute of Biophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences) for their contribution to 7.0T MRI data acquisition and Yadi Zhang and Xiaopeng Gu (Department of Ophthalmology, Peking University First Hospital) for their contribution to OCTA data acquisition. We appreciate the support of Weili Yang (Department of Neurology, Peking University First Hospital) for administrative assistance.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82101355, 82271323, and 82171059) and the scientific research seed fund of the Peking University first hospital (2021SF06).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yu Guo: conceptualization, formal analysis, and writing—original draft. Jianchen Hao: conceptualization, date curation, methodology, review, and editing. Ruilin Zhu: date curation methodology. Li Bai, Yong Shan, Yunchuang Sun, and Fan Li: date curation. Wei Zhang and Zhaoxia Wang: study design. Chen Ling: conceptualization, data curation, funding acquisition, writing, and editing. Liu Yang and Yun Yuan: funding acquisition, supervision, review, and editing. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This study was performed in line with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. Approval was granted by the Institutional Review Board and Ethics Committee at Peking University First Hospital.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, Y., Hao, J., Zhu, R. et al. Decreased retinal vascular density is associated with cognitive impairment in CADASIL: an optical coherence tomography angiography study. Neurol Sci (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-024-07390-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-024-07390-2