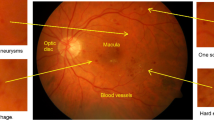
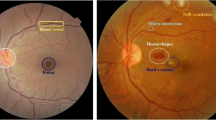
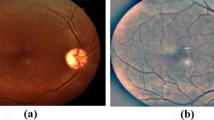
Abstract
Diabetic retinopathy, a microvascular condition associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease, poses a substantial global healthcare challenge. The demand for timely diagnosis has prompted the development of automated solutions due to the scarcity of specialists. In this paper, we introduce a ground-breaking approach to diabetic retinopathy detection – the Diabetic Retinopathy Residual Network (DR-ResNet +). The proposed model leverages the power of deep learning to automatically extract features, achieving optimal results in just seven training epochs. The DR-ResNet + architecture is meticulously designed by incorporating a series of convolutional, pooling, and fully connected layers. Hyperparameter optimization is done using both grid and random search techniques to ensure peak performance. To validate the proposed model’s robustness, simulated results are compared with well-established deep learning models, such as GoogleNet, VGG16, and AlexNet, using a comprehensive Kaggle dataset comprising over 35,000 retinal images. Moreover, the proposed model is also tested on external datasets like MESSIDOR and IDRiD for its validation. Simulation results reveal that the proposed DR-ResNet + model not only reduces training time by an impressive 95% but also exhibits outstanding performance metrics, including an accuracy of 0.9898, specificity of 0.9916, precision of 0.9670, sensitivity of 0.9829, and an F1-score of 0.9748. These findings position the proposed model as exceptionally well-suited for real-time clinical applications, offering a potential game-changer in diabetic retinopathy diagnosis. This paper presents DR-ResNet + as a pioneering advancement in diabetic retinopathy diagnosis. With its rapid training, superior accuracy, and significant real-world implications, the model holds promise for transforming the landscape of healthcare by providing timely and precise diagnoses for this critical condition.




















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article.
References
Kohner EM, Patel V, Rassam SM (1995) Role of blood flow and impaired autoregulation in the pathogenesis of diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes 44(6):603–608
Atkinson MA, Maclaren NK (1990) What causes diabetes? Sci Am 263(1):62–71
International Diabetes Federation (2021) IDF Diabetes Atlas, 10th edition. Retrieved from: https://www.diabetesatlas.org/
International Agency for the Prevention of Blindness (n.d.) Diabetic retinopathy. Retrieved from: https://www.iapb.org/learn/what-is-eye-health/diabetic-retinopathy/
Yau JW, Rogers SL, Kawasaki R, Lamoureux EL, Kowalski JW, Bek T, Wong TY (2012) Global prevalence and major risk factors of diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes Care 35(3):556–564. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc11-1909
Khan T, Bertram MY, Jina R, Mash B, Levitt N, Hofman K (2013) Preventing diabetes blindness: cost effectiveness of a screening programme using digital non-mydriatic fundus photography for diabetic retinopathy in a primary health care setting in South Africa. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 101(2):170–176
Wan S, Liang Y, Zhang Y (2018) Deep convolutional neural networks for diabetic retinopathy detection by image classification. Comput Electr Eng 72:274–282
Kumar S, Adarsh A, Kumar B, Singh AK (2020) An automated early diabetic retinopathy detection through improved blood vessel and optic disc segmentation. Opt Laser Technol 121:105815
Pao SI, Lin HZ, Chien KH, Tai MC, Chen JT, Lin GM (2020) Detection of diabetic retinopathy using bichannel convolutional neural network. J Ophthalmol 2020
Gayathri S, Gopi VP, Palanisamy P (2020) A lightweight CNN for Diabetic Retinopathy classification from fundus images. Biomed Signal Process Control 62:102115
Mateen M, Wen J, Hassan M, Nasrullah N, Sun S, Hayat S (2020) Automatic detection of diabetic retinopathy: a review on datasets, methods and evaluation metrics. IEEE Access 8:48784–48811
Jiang W, Chen Z, Xiang Y, Shao D, Ma L, Zhang J (2019) SSEM: A novel self-adaptive stacking ensemble model for classification. IEEE Access 7:120337–120349
Chetoui M, Akhloufi MA (2020) Explainable end-to-end deep learning for diabetic retinopathy detection across multiple datasets. J Med Imaging 7(4):044503–044503
Hinton GE, Srivastava N, Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Salakhutdinov RR (2012) Improving neural networks by preventing co-adaptation of feature detectors. arXiv preprint arXiv:1207.0580
Shanthi T, Sabeenian RS (2019) Modified Alexnet architecture for classification of diabetic retinopathy images. Comput Electr Eng 76:56–64
Mehrabi N, Morstatter F, Saxena N, Lerman K, Galstyan A (2021) A survey on bias and fairness in machine learning. ACM Comput Surv (CSUR) 54(6):1–35
Ruamviboonsuk P, Krause J, Chotcomwongse P, Sayres R, Raman R, Widner K, Webster DR (2019) Deep learning versus human graders for classifying diabetic retinopathy severity in a nationwide screening program. NPJ Digit Med 2(1):25
Kumar SA, Priya R, Sundararajan S (2021) Detection of diabetic retinopathy using bi-channel CNN. J Ambient Intell Humaniz Comput 12(9):8323–8331. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-021-03468-6
Kumari N, Kaur P (2021) LCNN for diabetic retinopathy classification. Multimed Tools Appl 80(8):12387–12408. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-020-10195-1
Garg S, Dubey SR, Koozekanani DD (2020) Exudate detection for diabetic retinopathy using pretrained convolutional neural networks. J Med Syst 44(2):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-019-1526-7
Kaggle (n.d.) Diabetic Retinopathy Detection. https://www.kaggle.com/c/diabetic-retinopathy-detection. Accessed 24 Apr 2022
Alzubaidi L, Zhang J, Humaidi AJ, Al-Dujaili A, Duan Y, Al-Shamma O, Farhan L (2021) Review of deep learning: Concepts, CNN architectures, challenges, applications, future directions. J Big Data 8:1–74
Zagoruyko S, Komodakis N (2016) Wide residual networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:1605.07146
Nayak SR, Nayak DR, Sinha U, Arora V, Pachori RB (2021) Application of deep learning techniques for detection of COVID-19 cases using chest X-ray images: A comprehensive study. Biomed Signal Process Control 64:102365
Bradley AP (1997) The use of the area under the ROC curve in the evaluation of machine learning algorithms. Pattern Recogn 30(7):1145–1159
Ioannidis JP, Tarone R, McLaughlin, JK (2011) The false-positive to false-negative ratio in epidemiologic studies. Epidemiology 450–456
Lam C, Yi D, Guo M, Lindsey T (2018) Automated detection of diabetic retinopathy using deep learning. AMIA Jt Summits Transl Sci Proc 2017:147–155
Pratt H, Coenen F, Broadbent DM, Harding SP, Zheng Y (2016) Convolutional neural networks for diabetic retinopathy. Procedia Comput Sci 90:200–205, SSN 1877–0509. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2016.07.014
Math L, Fatima R (2021) Adaptive machine learning classification for diabetic retinopathy. Multimed Tools Appl 80:5173–5186. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-020-09793-7
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J (2015) Deep residual learning for image recognition. arXiv preprint arXiv:1512.03385. Available at: https://arxiv.org/abs/1512.03385
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J (2016) Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (pp 770–778)
Yaqoob MK, Ali SF, Bilal M, Hanif MS, Al-Saggaf UM (2021) ResNet based deep features and random forest classifier for diabetic retinopathy detection. Sensors 21(11):3883
Almoosawi NM, A. M. M., Khudeyer RS (2021) ResNet-34/DR: a residual convolutional neural network for the diagnosis of diabetic retinopathy. Informatica 45(7)
Masood S, Luthra T, Sundriyal H, Ahmed M (2017) Identification of diabetic retinopathy in eye images using transfer learning. In 2017 international conference on computing, communication and automation (ICCCA) (pp 1183–1187). IEEE
Deshpande A, Pardhi J (2021) Automated detection of Diabetic Retinopathy using VGG-16 architecture. Irjet 8(03)
Wilkinson CP, Ferris FL III, Klein RE, Lee PP, Agardh CD, Davis M, Global Diabetic Retinopathy Project Group (2003) Proposed international clinical diabetic retinopathy and diabetic macular edema disease severity scales. Ophthalmology 110(9):1677–1682
Davis MD, Fisher MR, Gangnon RE, Barton F, Aiello LM, Chew EY, Knatterud GL (1998) Risk factors for high-risk proliferative diabetic retinopathy and severe visual loss: Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study Report# 18. Investig Ophthalmol Vis Sci 39(2):233–252
Porwal P, Pachade S, Kamble R, Kokare M, Deshmukh G, Sahasrabuddhe V, Meriaudeau F (2018) Indian diabetic retinopathy image dataset (IDRiD): a database for diabetic retinopathy screening research. Data 3(3):25
Decencière E, Zhang X, Cazuguel G et al (2014) Messidor Dataset- https://www.adcis.net/en/Download-Third-Party/Messidor.html
Shen D, Saab SS (2021) Noisy-output-based direct learning tracking control with Markov nonuniform trial lengths using adaptive gains. IEEE Trans Autom Control 67(8):4123–4130
Sayour MH, Kozhaya SE, Saab SS (2022) Autonomous robotic manipulation: Real-time, deep-learning approach for grasping of unknown objects. J Robot 2022
Shen D, Huo N, Saab SS (2021) A probabilistically quantized learning control framework for networked linear systems. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 33(12):7559–7573
Saab SS, Jaafar RH (2021) A proportional-derivative-double derivative controller for robot manipulators. Int J Control 94(5):1273–1285
Saab SS, Shen D, Orabi M, Kors D, Jaafar RH (2021) Iterative learning control: Practical implementation and automation. IEEE Trans Industr Electron 69(2):1858–1866
Dayan F, Rafiq M, Ahmed N, Baleanu D, Raza A, Ahmad MO, Iqbal M (2022) Design and numerical analysis of fuzzy nonstandard computational methods for the solution of rumor based fuzzy epidemic model. Physica A 600:127542
Kouatli I (2020) The use of fuzzy logic as augmentation to quantitative analysis to unleash knowledge of participants’ uncertainty when filling a survey: case of cloud computing. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 34(3):1489–1500
Ben Abdallah S, Kouatli I (2020) Fuzzy Volatility of Project Option Value Based on Trapezoidal Membership Functions. In Intelligent and Fuzzy Techniques in Big Data Analytics and Decision Making: Proceedings of the INFUS 2019 Conference, Istanbul, Turkey, July 23–25, 2019 (pp 1307–1314). Springer International Publishing
Abdallah SB, Kouatli I (2018) Fuzzy volatility effect on major projects timing. In 2018 IEEE International Conference on Fuzzy Systems (FUZZ-IEEE) (pp 1–6). IEEE
Azadeh A, Kalantari M, Ahmadi G, Eslami H (2019) A flexible genetic algorithm-fuzzy regression approach for forecasting: The case of bitumen consumption. Constr Innov 19(1):71–88
Taheri R, Kabuli M, Vryzas Z (2020) Fracturing and permeability enhancement with laser technology employing fuzzy logic. J Petrol Sci Eng 188:106830
Kouatli I (2018) Fuzzimetric employee evaluations system (FEES): A multivariable-modular approach. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 35(4):4717–4729
Salloum G, Tekli J (2021) Automated and personalized nutrition health assessment, recommendation, and progress evaluation using fuzzy reasoning. Int J Hum Comput Stud 151:102610
Abboud R, Tekli J (2020) Integration of nonparametric fuzzy classification with an evolutionary-developmental framework to perform music sentiment-based analysis and composition. Soft Comput 24(13):9875–9925
Ghanem CR, Gereige EN, Bou Nader WS, Mansour CJ (2022) Stirling system optimization for series hybrid electric vehicles. Proc Inst Mech Eng D: J Automob Eng 236(2–3):407–423
Abbas N, Fawaz W, Sharafeddine S, Mourad A, Abou-Rjeily C (2022) SVM-based task admission control and computation offloading using lyapunov optimization in heterogeneous MEC network. IEEE Trans Netw Serv Manage 19(3):3121–3135
Marrouche W, Farah R, Harmanani HM (2018) A multiobjective optimization method for the SOC test time, TAM, and power optimization using a strength pareto evolutionary algorithm. In Information Technology-New Generations: 14th International Conference on Information Technology (pp 685–695). Springer International Publishing
Yusuf A, Sulaiman TA, Alshomrani AS, Baleanu D (2022) Optical solitons with nonlinear dispersion in parabolic law medium and three-component coupled nonlinear Schrödinger equation. Opt Quant Electron 54(6):390
Issa JS (2022) A nonlinear absorber for the reflection of travelling waves in bars. Nonlinear Dyn 108(4):3279–3295
Tiwari AK, Bathia D, Bouri E, Gupta R (2021) Investor sentiment connectedness: evidence from linear and nonlinear causality approaches. Ann Financ Econ 16(04):2150016
Chamoun S, Nour C (2021) A nonlinear ϕ0-convexity result for the bilateral minimal time function
Kassis MT, Tannir D, Toukhtarian R, Khazaka R (2019) Moments-based sensitivity analysis of x-parameters with respect to linear and nonlinear circuit components. In 2019 IEEE 28th Conference on Electrical Performance of Electronic Packaging and Systems (EPEPS) (pp 1–3). IEEE
Saab SS, Saab KK (2019) Shuffled linear regression with erroneous observations. In 2019 53rd Annual Conference on Information Sciences and Systems (CISS) (pp 1–6). IEEE
Bouri E, Gupta R, Wang S (2022) Nonlinear contagion between stock and real estate markets: International evidence from a local Gaussian correlation approach. Int J Financ Econ 27(2):2089–2109
Hussain M, Kaassamani S, Auguste T, Boutu W, Gauthier D, Kholodtsova M, Merdji H (2021) Spectral control of high order harmonics through non-linear propagation effects. Appl Phys Lett 119(7)
Haraty RA, Mansour N, Zeitunlian H (2018) Metaheuristic algorithm for state-based software testing. Appl Artif Intell 32(2):197–213
Tarhini A, Harfouche A, De Marco M (2022) Artificial intelligence-based digital transformation for sustainable societies: the prevailing effect of COVID-19 crises. Pac Asia J Assoc Inf Syst 14(2):1
Nour C, Takche J (2020) A general result about inner regularization of sets
Chicha E, Bouna BA, Nassar M, Chbeir R, Haraty RA, Oussalah M, Alraja MN (2021) A user-centric mechanism for sequentially releasing graph datasets under blowfish privacy. ACM Trans Internet Technol (TOIT) 21(1):1–25
Mourad A, Tout H, Wahab OA, Otrok H, Dbouk T (2020) Ad hoc vehicular fog enabling cooperative low-latency intrusion detection. IEEE Internet Things J 8(2):829–843
AbdulRahman S, Tout H, Mourad A, Talhi C (2020) FedMCCS: Multicriteria client selection model for optimal IoT federated learning. IEEE Internet Things J 8(6):4723–4735
Rahman SA, Tout H, Talhi C, Mourad A (2020) Internet of things intrusion detection: Centralized, on-device, or federated learning? IEEE Network 34(6):310–317
Khabbaz M, Assi C, Sharafeddine S (2021) Multihop V2U path availability analysis in UAV-assisted vehicular networks. IEEE Internet Things J 8(13):10745–10754
Sorkhoh I, Ebrahimi D, Assi C, Sharafeddine S, Khabbaz M (2020) An infrastructure-assisted workload scheduling for computational resources exploitation in the fog-enabled vehicular network. IEEE Internet Things J 7(6):5021–5032
Arafeh M, El Barachi M, Mourad A, Belqasmi F (2019) A blockchain based architecture for the detection of fake sensing in mobile crowdsensing. In 2019 4th International Conference on Smart and Sustainable Technologies (SpliTech) (pp 1–6). IEEE
Haraty RA, Boukhari B, Kaddoura S (2021) An effective hash-based assessment and recovery algorithm for healthcare systems. Arab J Sci Eng 1–14
Yunis M, Markarian C, El-Kassar AN (2020) A conceptual model for sustainable adoption of ehealth: Role of digital transformation culture and healthcare provider’s readiness. Proceedings of the IMCIC, 17
Helwan A, Ma’aitah MKS, Uzelaltinbulat S, Altobel MZ, Darwish M (2021) Gaze prediction based on convolutional neural network. In International conference on emerging technologies and intelligent systems (pp 215–224). Cham: Springer International Publishing
Gerges F, Shih F, Azar D (2021) Automated diagnosis of acne and rosacea using convolution neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2021 4th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Pattern Recognition (pp 607–613)
Abbas N, Nasser Y, Shehab M, Sharafeddine S (2021) Attack-specific feature selection for anomaly detection in software-defined networks. In 2021 3rd IEEE middle east and north africa communications conference (menacomm) (pp 142–146). IEEE
Tarhini A, Danach K, Harfouche A (2022) Swarm intelligence-based hyper-heuristic for the vehicle routing problem with prioritized customers. Ann Oper Res 1–22
Zhou Z, Li Y, Li J, Yu K, Kou G, Wang M, Gupta BB (2022) Gan-siamese network for cross-domain vehicle re-identification in intelligent transport systems. IEEE Trans Netw Sci Eng
Kfouri R (2023) A Robust Deep Learning Approach for Distribution System State Estimation with Distributed Generation (Doctoral dissertation, Lebanese American University)
Rehan M, Javed AR, Kryvinska N, Gadekallu TR, Srivastava G, Jalil Z (2023) Supply Chain Management Using an Industrial Internet of Things Hyperledger Fabric Network. Hum-Centric Comput Inf Sci 13
Zhang Z, Jiang H, Shen D, Saab SS (2024) Data-Driven Learning Control Algorithms for Unachievable Tracking Problems. IEEE/CAA J Autom Sin 11(1):1–14
Saab S Jr, Phoha S, Zhu M, Ray A (2022) An adaptive polyak heavy-ball method. Mach Learn 111(9):3245–3277
Saab S Jr, Saab K, Phoha S, Zhu M, Ray A (2022) A multivariate adaptive gradient algorithm with reduced tuning efforts. Neural Netw 152:499–509
Saab S Jr, Fu Y, Ray A, Hauser M (2022) A dynamically stabilized recurrent neural network. Neural Process Lett 54(2):1195–1209
Kozhaya SE, Haidar-Ahmad JA, Abdallah AA, Kassas ZM, Saab SS (2021) Comparison of neural network architectures for simultaneous tracking and navigation with LEO satellites. In Proceedings of the 34th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of The Institute of Navigation (ION GNSS+ 2021) (pp 2507–2520)
Funding
No funding was received for conducting this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Conflicts of interest
None.
Research involving human participants and/or animals
None.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Baba, S.M., Bala, I., Dhiman, G. et al. Automated diabetic retinopathy severity grading using novel DR-ResNet + deep learning model. Multimed Tools Appl (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-024-18434-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-024-18434-2